We have n jobs, where every job is scheduled to be done from startTime[i] to endTime[i], obtaining a profit of profit[i].
You're given the startTime, endTime and profit arrays, return the maximum profit you can take such that there are no two jobs in the subset with overlapping time range.
If you choose a job that ends at time X you will be able to start another job that starts at time X.
Example 1:
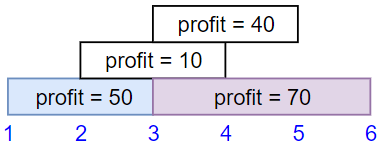
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,3], endTime = [3,4,5,6], profit = [50,10,40,70] Output: 120 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first and fourth job. Time range [1-3]+[3-6] , we get profit of 120 = 50 + 70.
Example 2:
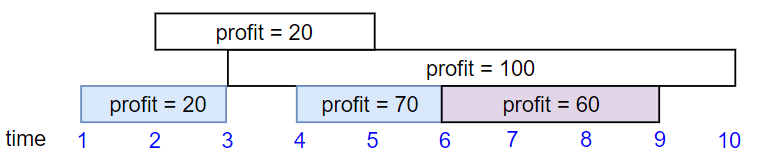
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,4,6], endTime = [3,5,10,6,9], profit = [20,20,100,70,60] Output: 150 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first, fourth and fifth job. Profit obtained 150 = 20 + 70 + 60.
Example 3:
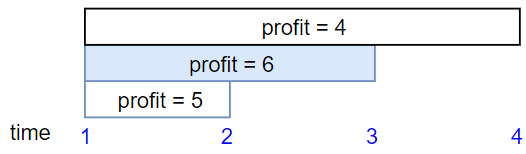
Input: startTime = [1,1,1], endTime = [2,3,4], profit = [5,6,4] Output: 6
Constraints:
1 <= startTime.length == endTime.length == profit.length <= 5 * 1041 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <= 1091 <= profit[i] <= 104
My answer: basically, it is sorting by end time, and look for the nearest job which is compatible with current job via BS, and find if including or excluding current job can produce max profit at ith element.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 | class Solution { class Job { public int start; public int end; public int profit; public Job(int start, int end, int profit) { this.start = start; this.end = end; this.profit = profit; } } public int jobScheduling(int[] startTime, int[] endTime, int[] profit) { if (profit == null) { return 0; } if (profit.length == 1) { return profit[0]; } List<Job> jobs = new ArrayList<Job>(); for (int i = 0; i < profit.length; i ++) { jobs.add(new Job(startTime[i], endTime[i], profit[i])); } Collections.sort(jobs, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a.end, b.end)); // dp is max profit from 0 to ith element // only 2 choices: including ith or excluding ith // if including ith, look for nearest compatible job plus ith value // if excluding ith, use dp[i - 1] int[] dp = new int[jobs.size()]; dp[0] = jobs.get(0).profit; for (int i = 1; i < jobs.size(); i ++) { dp[i] = jobs.get(i).profit; int j = bs(jobs, 0, i, jobs.get(i)); if (j == -1) { dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], jobs.get(i).profit); } else { dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], dp[j] + jobs.get(i).profit); } } return dp[jobs.size() - 1]; } // find the rightmost job which can be scheduled before target private int bs(List<Job> jobs, int l, int r, Job target) { while(l < r) { int m = (l + r)/2; Job mid = jobs.get(m); if (mid.end <= target.start) { l = m + 1; } else { r = m; } } return (l - 1); } private int helper(int currentIndex, List<Job> jobs, List<Job> selectedJobs) { if (currentIndex == jobs.size()) { int profitSum = 0; for (Job job : selectedJobs) { profitSum += job.profit; } return profitSum; } int max = 0; if (canFit(selectedJobs.get(selectedJobs.size() - 1), jobs.get(currentIndex))) { selectedJobs.add(jobs.get(currentIndex)); max = helper(currentIndex + 1, jobs, selectedJobs); // back track selectedJobs.remove(selectedJobs.size() - 1); max = Math.max(max, helper(currentIndex + 1, jobs, selectedJobs)); } else { // cannot fit max = helper(currentIndex + 1, jobs, selectedJobs); } return max; } private boolean canFit(Job lastJob, Job currentJob) { return lastJob.end <= currentJob.start; } } |
No comments:
Post a Comment